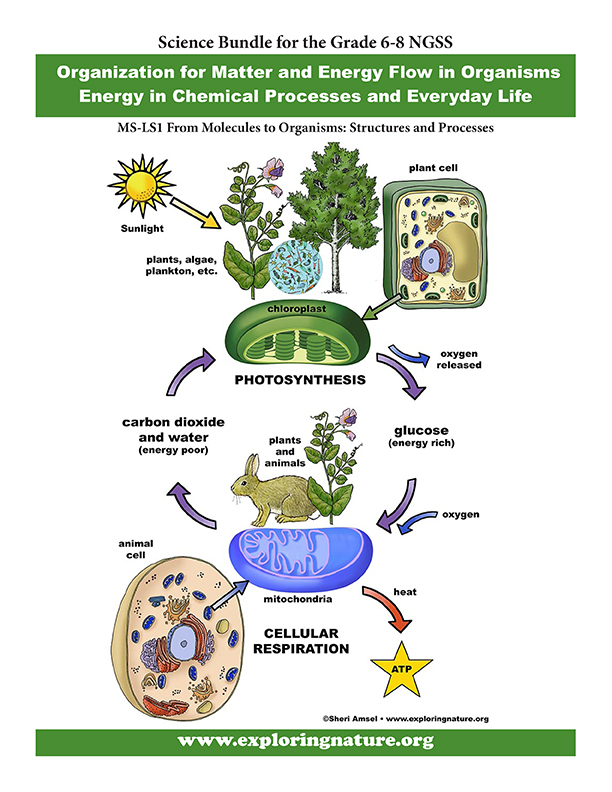
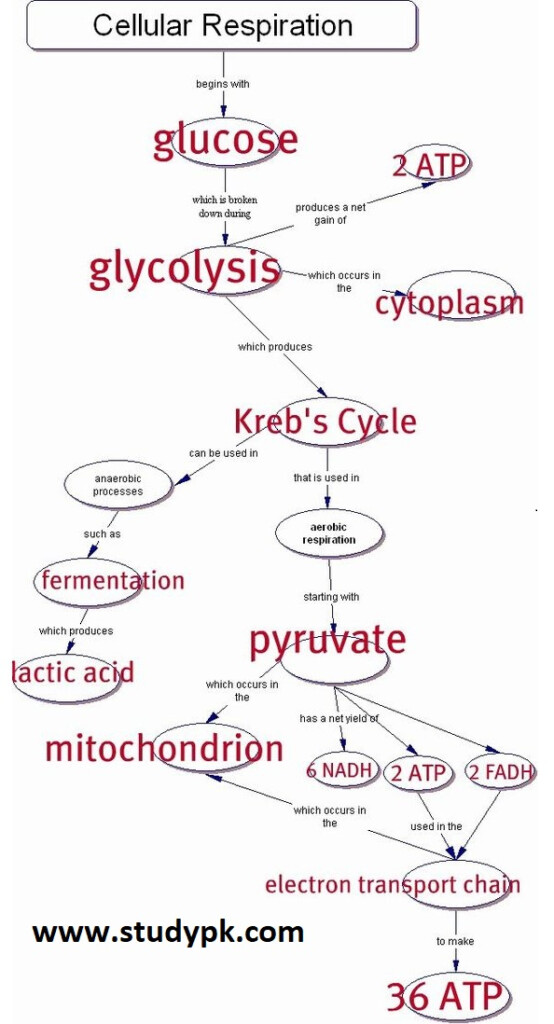
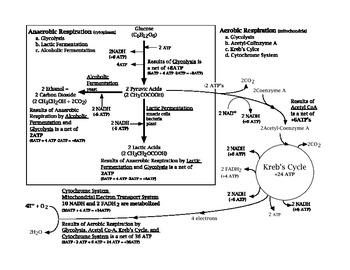
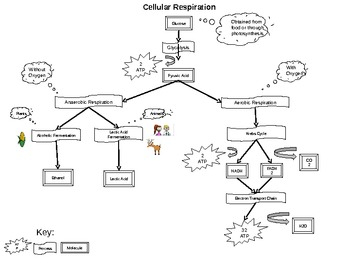
Cellular respiration is the process by which cells in living organisms break down glucose to produce energy in the form of ATP (adenosine triphosphate). This energy is essential for the functioning of cells and is used for various biological processes. The flow chart of cellular respiration can be broken down into three main stages: glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation.
Glycolysis is the first stage of cellular respiration and takes place in the cytoplasm of the cell. In this stage, glucose is broken down into two molecules of pyruvate, producing a small amount of ATP and NADH. The pyruvate molecules then enter the mitochondria to continue the process of cellular respiration.
Flow Chart Of Cellular Respiration
The Citric Acid Cycle
Once inside the mitochondria, the pyruvate molecules undergo a series of chemical reactions known as the citric acid cycle. During this stage, carbon dioxide is produced, and more ATP and NADH are generated. The citric acid cycle is a crucial step in the production of energy for the cell.
Oxidative Phosphorylation
The final stage of cellular respiration is oxidative phosphorylation, which takes place in the inner membrane of the mitochondria. During this stage, the NADH and FADH2 molecules produced in glycolysis and the citric acid cycle are used to create a proton gradient across the membrane. This gradient is then used by the enzyme ATP synthase to produce a large amount of ATP, the main energy currency of the cell.
Overall, the flow chart of cellular respiration illustrates the complex process by which cells generate energy from glucose. Understanding this process is essential for understanding how living organisms function at a cellular level.
Download Flow Chart Of Cellular Respiration
Biology Flow Chart For Cellular Respiration StudyPK
Cellular Respiration Flow Chart By Curtis Lynch TpT
Cellular Respiration Flow Chart Worksheet Worksheets For Kindergarten
Cellular Respiration Flow Chart Activity By Kristi Hancock TpT