Float glass is a type of glass made by floating molten glass on a bed of molten metal, typically tin. This process results in glass with a uniform thickness and a flat surface, making it ideal for a variety of applications such as windows, doors, and mirrors.
The float glass process begins with the raw materials, including silica sand, soda ash, limestone, and other additives, being mixed together and melted in a furnace. Once the glass is molten, it is poured onto a bath of molten tin, where it spreads out and forms a smooth, continuous ribbon.
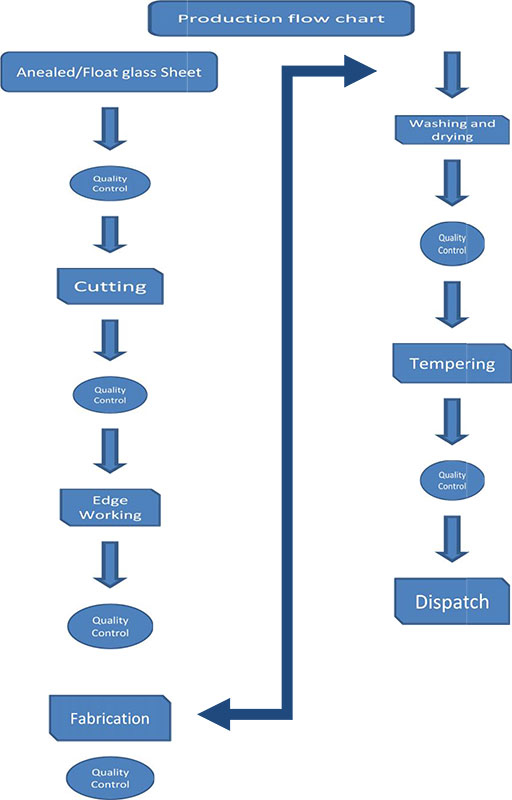
Float Glass Process Flow Chart
2. Steps in the Float Glass Process
1. Melting: The raw materials are melted in a furnace at temperatures exceeding 1700 degrees Celsius to form molten glass.
2. Floating: The molten glass is poured onto a bath of molten tin, where it spreads out and forms a continuous ribbon.
3. Annealing: The glass ribbon is slowly cooled in a temperature-controlled lehr to relieve internal stresses and improve strength.
4. Cutting: The cooled glass ribbon is cut into desired sizes and shapes using automated cutting machines.
5. Inspecting: The cut glass pieces are inspected for defects and imperfections before being packaged and shipped to customers.
3. Conclusion
The float glass process flow chart outlines the key steps involved in producing high-quality float glass. By following a strict set of procedures and quality control measures, manufacturers can ensure that the glass produced meets the required standards for clarity, strength, and uniformity.
Whether you are in the construction industry or the automotive sector, understanding the float glass process flow chart can help you appreciate the complexity and precision involved in manufacturing this versatile material.