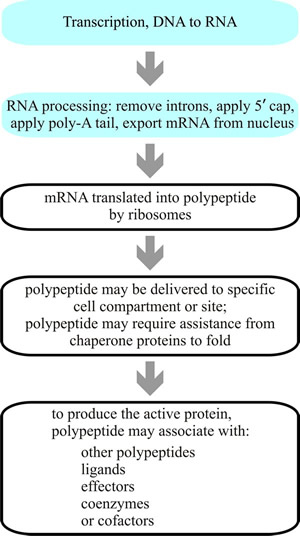
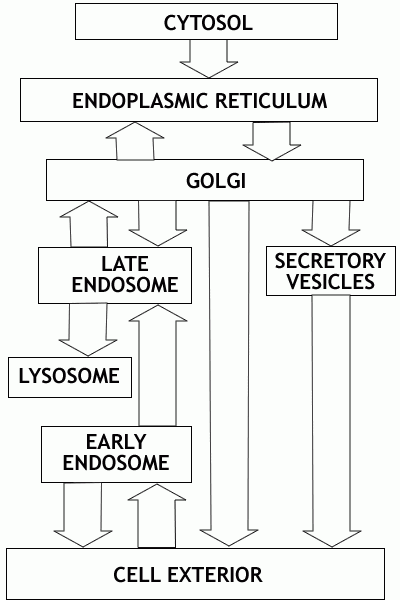
The endomembrane system is a network of membranes found in eukaryotic cells that work together to carry out various cellular functions. This system includes the nuclear envelope, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, lysosomes, vesicles, and plasma membrane. The components of the endomembrane system are interconnected and work in coordination to transport molecules, produce proteins, and break down cellular waste.
The flow chart of the endomembrane system illustrates the pathways and processes involved in the movement of molecules and proteins within the cell. Understanding this flow chart can help in comprehending the intricate mechanisms that occur within cells and how they contribute to the overall function of the organism.
Flow Chart Of Endomembrane System
Components of the Endomembrane System
Nuclear Envelope: The nuclear envelope surrounds the nucleus of the cell and consists of two membranes. It regulates the passage of molecules in and out of the nucleus through nuclear pores.
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER): The ER is a network of membranes that extends throughout the cell. It is divided into rough ER, which is studded with ribosomes and involved in protein synthesis, and smooth ER, which is responsible for lipid synthesis and detoxification.
Golgi Apparatus: The Golgi apparatus is responsible for modifying, sorting, and packaging proteins for transport within the cell or secretion outside the cell. It consists of flattened membrane-bound sacs called cisternae.
Lysosomes: Lysosomes are membrane-bound organelles that contain digestive enzymes. They break down cellular waste, old organelles, and foreign substances that enter the cell.
Vesicles: Vesicles are small membrane-bound sacs that transport molecules within the cell or to the cell membrane for secretion. They are involved in processes such as endocytosis, exocytosis, and intracellular transport.
Plasma Membrane: The plasma membrane surrounds the cell and regulates the passage of molecules in and out of the cell. It is composed of a phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins that help in cell signaling and transport.
By understanding the flow chart of the endomembrane system and the functions of its components, researchers can gain insights into the cellular processes that are essential for the survival and function of eukaryotic organisms.
Overall, the endomembrane system plays a crucial role in maintaining cellular homeostasis, regulating protein synthesis and transport, and facilitating communication between cells. Its intricate network of membranes and organelles work together seamlessly to ensure the proper function of cells and organisms as a whole.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the flow chart of the endomembrane system provides a visual representation of the interconnected pathways and processes that occur within eukaryotic cells. By studying this flow chart and understanding the functions of its components, researchers can unravel the complexities of cellular biology and gain a deeper appreciation for the intricate mechanisms that govern life at the cellular level.
Download Flow Chart Of Endomembrane System
Endomembrane System Flow Chart
Endomembrane System Flow Chart
Endomembrane System Flow Chart
Endomembrane System Flow Chart