Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are a common and often painful condition that can affect anyone at any age. Understanding the pathophysiology of UTIs is crucial in effectively diagnosing and treating this condition.
UTIs typically occur when bacteria enter the urinary tract through the urethra and multiply in the bladder. The most common bacteria responsible for UTIs is Escherichia coli (E. coli), which is normally found in the gastrointestinal tract. Women are more prone to UTIs due to their shorter urethra, which allows bacteria to reach the bladder more easily.
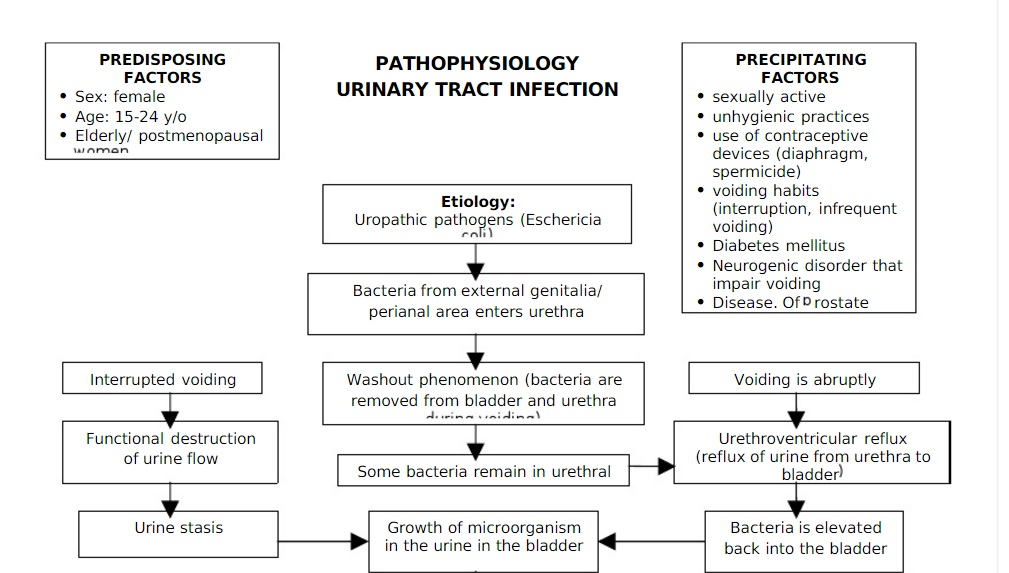
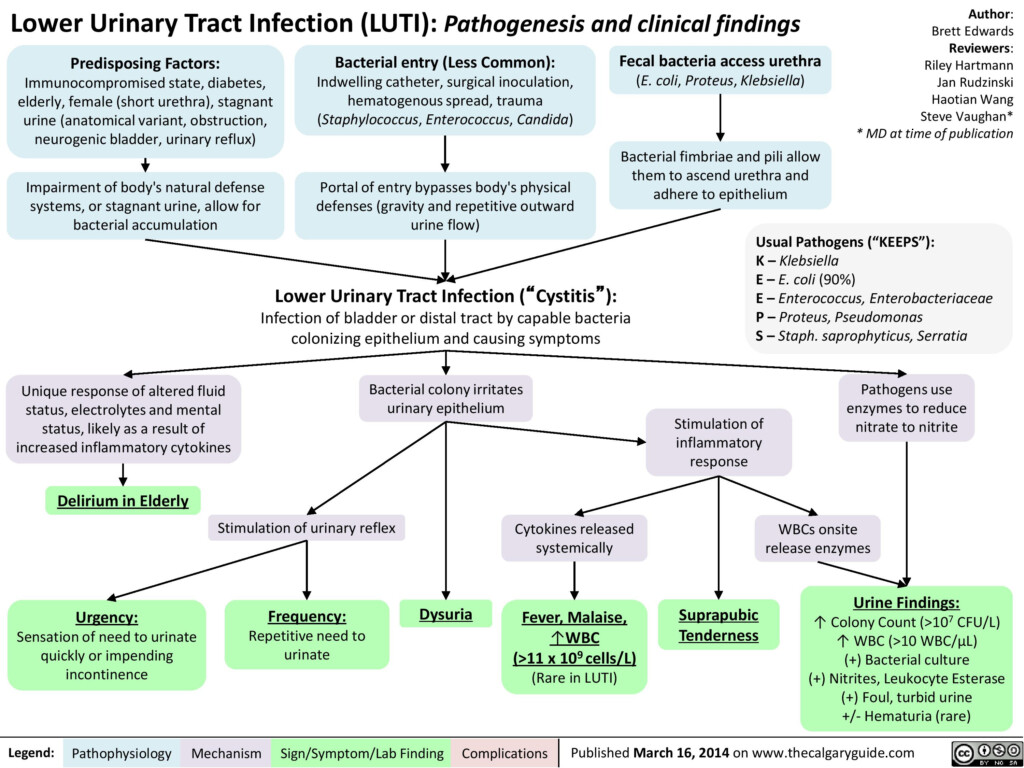
Flow Chart Pathophysiology Of Urinary Tract Infection
Flow Chart Illustrating the Pathophysiology of UTIs
A flow chart illustrating the pathophysiology of UTIs can help visualize the sequence of events that lead to infection. The flow chart typically starts with the entry of bacteria through the urethra and progresses to colonization of the bladder, causing inflammation and symptoms such as frequent urination, burning sensation during urination, and cloudy or foul-smelling urine.
If left untreated, UTIs can progress to more severe infections, such as pyelonephritis (infection of the kidneys), which can lead to serious complications. Proper diagnosis and treatment of UTIs are essential in preventing these complications and relieving symptoms.
Treatment and Prevention of UTIs
Treatment of UTIs usually involves antibiotics to eliminate the bacteria causing the infection. It is important to complete the full course of antibiotics as prescribed by a healthcare provider to ensure that the infection is completely eradicated.
Prevention of UTIs includes staying hydrated, practicing good hygiene, and urinating after intercourse to flush out bacteria. Cranberry juice or supplements may also help prevent UTIs by preventing bacteria from adhering to the bladder wall. By understanding the pathophysiology of UTIs and taking preventive measures, individuals can reduce their risk of developing this common infection.
Download Flow Chart Pathophysiology Of Urinary Tract Infection
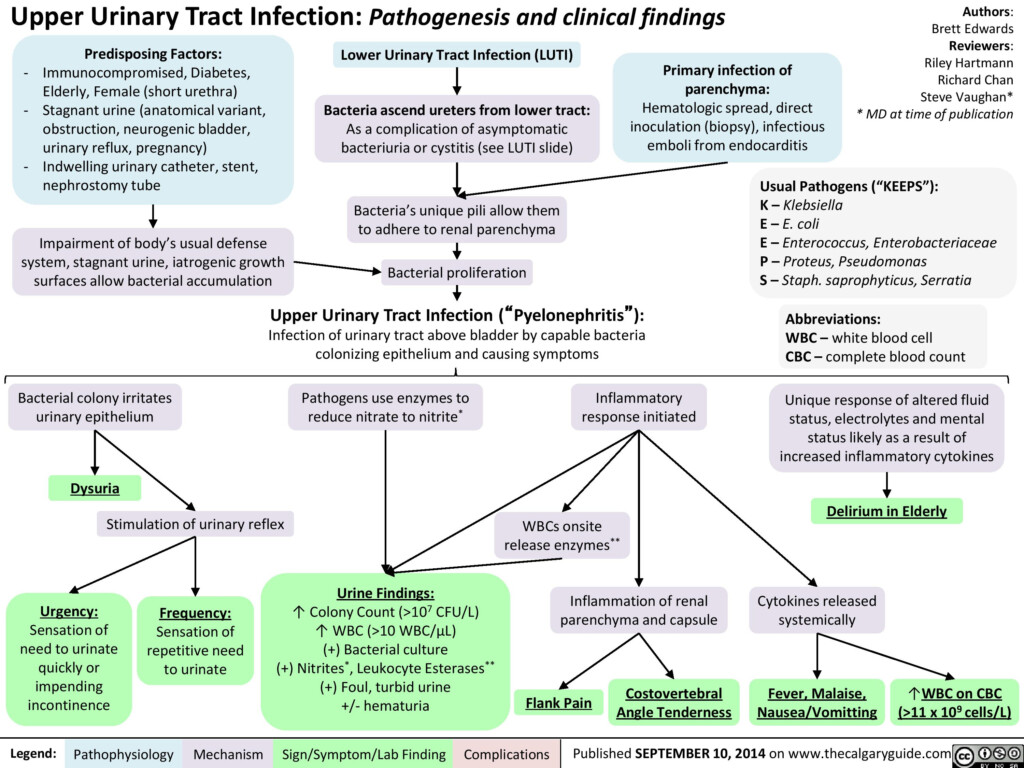
Upper Urinary Tract Infection UUTI Pathogenesis And Clinical
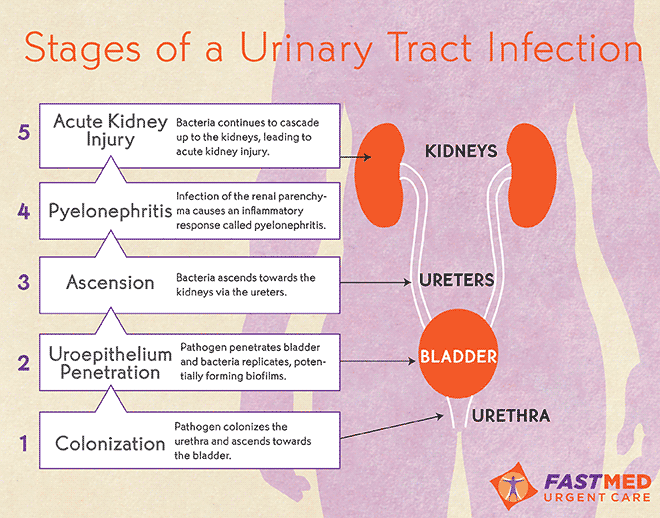
Urinary Tract Infection UTI FastMed
Upper Urinary Tract Infection UUTI Pathogenesis And Clinical
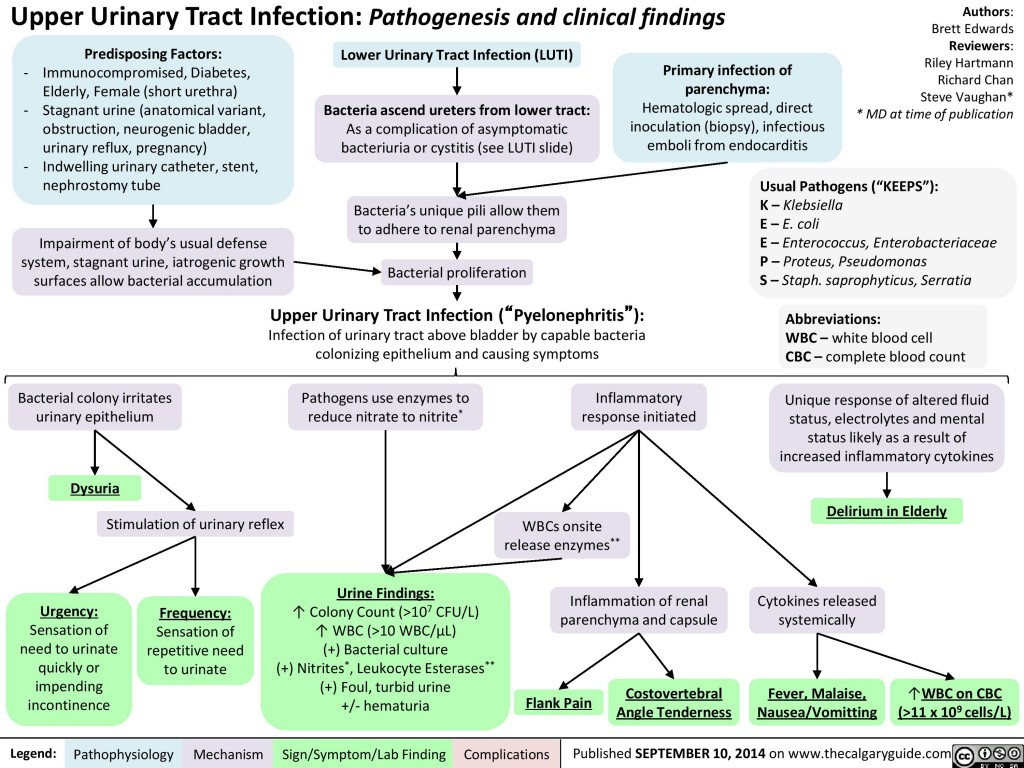
Lower Urinary Tract Infection Pathogenesis And Clinical Findings