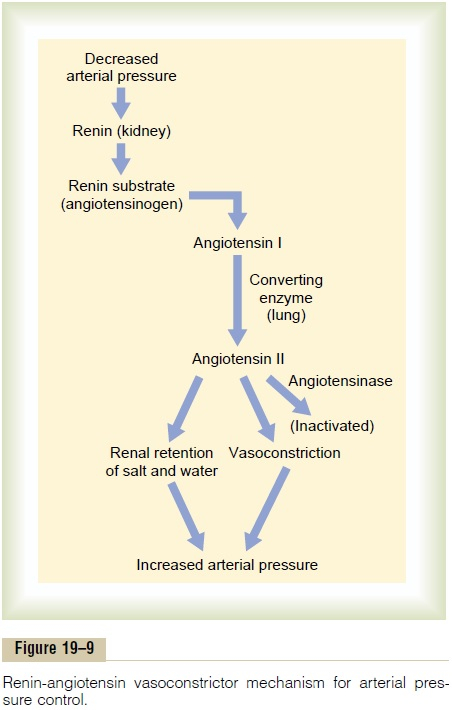
The Renin Angiotensin System (RAS) is a crucial regulatory system that helps to maintain blood pressure and fluid balance in the body. The system starts with the release of renin from the kidneys in response to low blood pressure or low sodium levels. Renin acts on angiotensinogen, a protein produced by the liver, to convert it into angiotensin I.
Angiotensin I is then converted into angiotensin II by the enzyme angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE), which is mainly found in the lungs. Angiotensin II is a potent vasoconstrictor, meaning it causes blood vessels to constrict, leading to an increase in blood pressure. It also stimulates the release of aldosterone from the adrenal glands, which helps to retain sodium and water in the body.
Renin Angiotensin System Flow Chart
Key Components of the Renin Angiotensin System
1. Renin: Produced by the kidneys, renin is an enzyme that plays a crucial role in initiating the RAS cascade by converting angiotensinogen into angiotensin I.
2. Angiotensinogen: Produced by the liver, angiotensinogen is a protein that is converted into angiotensin I by renin.
3. Angiotensin I: Formed by the action of renin on angiotensinogen, angiotensin I is further converted into angiotensin II by ACE.
4. Angiotensin II: The active form of angiotensin, angiotensin II is a potent vasoconstrictor that increases blood pressure and stimulates the release of aldosterone.
Regulation of the Renin Angiotensin System
The RAS is tightly regulated to ensure that blood pressure and fluid balance are maintained within normal limits. Factors such as blood pressure, sodium levels, and hormonal signals can all influence the activity of the system. For example, high blood pressure or high sodium levels can inhibit the release of renin, while low blood pressure or low sodium levels can stimulate its release.
In conclusion, the Renin Angiotensin System is a complex regulatory system that plays a crucial role in maintaining blood pressure and fluid balance in the body. Understanding the flow chart of this system can help to shed light on how various components interact to achieve this important physiological function.